When it comes to understanding skin conditions, many people confuse a pilonidal abscess and a pilonidal cyst. While these two terms may seem similar, they are distinct, each with its characteristics, symptoms, and treatments. In this blog, we will explore the pilonidal abscess vs cyst comparison in detail, discussing what they are, how they differ, how to treat them, and when to seek medical attention.
What Is a Pilonidal Cyst?
A pilonidal cyst is a small sac that forms just beneath the skin, often at the top of the crease of the buttocks, near the tailbone. It usually contains hair, skin cells, and sometimes debris. Pilonidal cysts are quite common, and they can appear in anyone, but they tend to affect people between the ages of 15 and 30, especially men.
The cysts typically form when hair follicles become trapped beneath the skin, leading to the development of the cyst. However, not all pilonidal cysts are problematic. In many cases, a pilonidal cyst can remain asymptomatic, causing no pain or discomfort for long periods. People may only become aware of the cyst if it becomes infected or irritated.
What Is a Pilonidal Abscess?
A pilonidal abscess, on the other hand, occurs when a pilonidal cyst becomes infected. When the cyst becomes blocked, bacteria can multiply, causing the formation of pus within the cyst. The buildup of pus leads to swelling, intense pain, and inflammation. Pilonidal abscesses are often very painful and require more immediate medical intervention.
While a pilonidal cyst may not always cause symptoms, an abscess is a painful condition that can make sitting, walking, or even standing difficult. When left untreated, pilonidal abscesses can lead to more serious complications, including the spread of infection to surrounding tissue.
Pilonidal Abscess vs Cyst: Key Differences
The main distinction between a pilonidal abscess vs cyst is the presence of infection. Below are the key differences:
Pilonidal Cyst:
- A pilonidal cyst is a non-infected sac that forms beneath the skin.
- It can remain painless and asymptomatic unless it becomes infected or inflamed.
- Treatment usually involves draining or surgical removal if the cyst causes pain or recurrent problems.
Pilonidal Abscess:
- A pilonidal abscess is an infected cyst filled with pus.
- It is often very painful, swollen, and tender to the touch.
- Treatment typically involves drainage of the abscess and possibly antibiotics to prevent further infection.
Symptoms of a Pilonidal Cyst
As mentioned, pilonidal cysts often do not cause symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, if a cyst becomes infected or inflamed, symptoms can develop. These include:
- Pain: The affected area may feel sore or tender, especially when sitting or applying pressure.
- Redness and Swelling: The skin over the cyst may become red and swollen.
- Drainage: A pilonidal cyst may start to leak fluid, pus, or blood, indicating that it has become infected.
- Foul Odor: Infected cysts may emit a foul-smelling discharge.
Symptoms of a Pilonidal Abscess
The symptoms of a pilonidal abscess are more pronounced and often require prompt medical attention. These include:
- Severe Pain: The area around the tailbone may become extremely painful, especially when sitting or moving.
- Swelling and Redness: The cyst becomes visibly swollen and may appear inflamed.
- Fever: An infection may lead to a fever, indicating that the body is fighting the infection.
- Pus Drainage: A pilonidal abscess will often drain thick, yellow, or greenish pus.
- Tightness: The area may feel tight and firm due to the accumulation of pus.
Causes of a Pilonidal Cyst and Abscess
Both pilonidal cysts and abscesses are associated with the following risk factors:
- Hair: Hair in the area can become trapped under the skin, leading to the formation of a cyst.
- Prolonged Sitting: People who sit for long periods (such as truck drivers or office workers) may be more prone to developing pilonidal cysts due to friction.
- Poor Hygiene: Improper hygiene may contribute to the development of a pilonidal cyst or abscess.
- Obesity: Excess weight can create more friction in the buttocks region, increasing the likelihood of a cyst forming.
- Family History: There may be a genetic predisposition for developing pilonidal cysts.
A pilonidal abscess occurs when the cyst becomes infected by bacteria, usually from the skin or surrounding area. It may also result from excessive friction or sweating.
Treatment for Pilonidal Cysts
Treatment for a pilonidal cyst depends on the severity of the symptoms. In some cases, the cyst may not need any treatment if it remains asymptomatic. However, when treatment is needed, options include:
Drainage: A healthcare provider may drain the cyst if it becomes painful or infected. This involves making a small incision to release the fluid or pus trapped inside.
Surgical Removal: If the cyst is recurrent or causing significant discomfort, surgical removal may be recommended.
Antibiotics: If an infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear up the infection.
Treatment for Pilonidal Abscesses
The treatment for a pilonidal abscess is more urgent and requires immediate medical attention. Treatment options may include:
Incision and Drainage (I&D): The abscess will need to be drained to remove the pus and relieve pressure. This procedure is typically done in a medical office or clinic.
Antibiotics: If the abscess is large or there is concern about spreading infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to fight the infection.
Surgical Removal: In some cases, the abscess may require surgical removal of the cyst along with the surrounding tissue to prevent further abscess formation.
After the abscess is drained or surgically treated, it may take several weeks to fully heal. During this time, proper wound care and hygiene are essential to avoid re-infection.
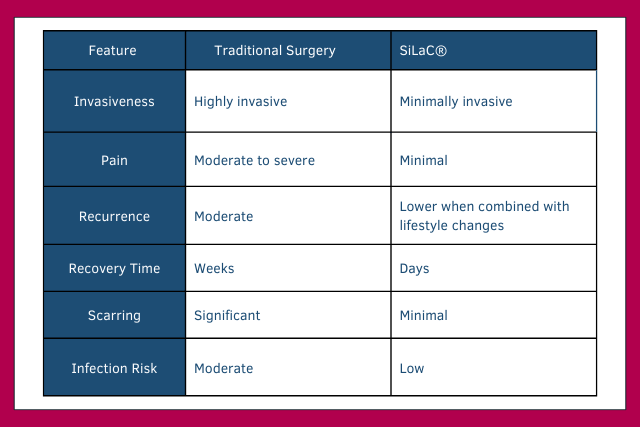
Sinus Laser-Assisted Closure (SiLaC®): A Minimally Invasive Treatment for Pilonidal Disease
Sinus Laser-Assisted Closure (SiLaC®) is a minimally invasive treatment for pilonidal cysts and abscesses. It uses a laser to close sinus tracts and cysts, promoting faster healing and reducing the risk of recurrence. SiLaC® is ideal for patients with chronic pilonidal disease, offering a quicker recovery compared to traditional surgery. It’s less invasive, involves a small incision, and requires minimal post-operative care. While traditional surgery is effective, SiLaC® provides an alternative with fewer risks and faster recovery, making it a great option for many patients dealing with pilonidal conditions.
Preventing Pilonidal Cysts and Abscesses
While pilonidal cysts are not always preventable, the following steps can reduce the risk of developing them:
- Good Hygiene: Keep the area clean and dry to reduce the chances of hair becoming trapped under the skin.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: If you must sit for long periods, take breaks to stand and move around.
- Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the friction that may contribute to the formation of cysts.
- Shaving or Trimming Hair: In some cases, trimming or shaving the hair around the tailbone can help prevent hair from becoming trapped in the skin.
Conclusion: Pilonidal Abscess vs Cyst
In summary, while both a pilonidal abscess vs cyst involve similar underlying conditions, the key difference lies in the infection. A pilonidal cyst is a non-infected sac that may or may not cause symptoms, while a pilonidal abscess is a painful, infected cyst that requires immediate treatment.
If you notice symptoms of a pilonidal cyst or abscess, it’s important to seek medical attention to prevent further complications. Treatment options, including drainage, antibiotics, and surgery, can help manage both conditions and provide relief.
Understanding the difference between a pilonidal abscess and cyst is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. If you’re dealing with either of these conditions, speak with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for your health.