Internal hemorrhoids are swollen veins located inside the rectum. Unlike external hemorrhoids, they usually do not cause pain, but they can lead to discomfort, bleeding, and complications if left untreated. Millions of people worldwide experience internal hemorrhoids at some point in their lives, making it a common gastrointestinal concern.
In Tampa and other regions, many patients seek information on effective treatments. These range from lifestyle adjustments to minimally invasive procedures, such as Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP®). This guide explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for internal hemorrhoids to help patients make informed healthcare decisions.
What Are Internal Hemorrhoids?
Internal hemorrhoids develop inside the rectum, above the anal sphincter. They differ from external hemorrhoids, which occur under the skin around the anus. They’re are often painless, but they may bleed or protrude, causing discomfort.
How Internal Hemorrhoids Form
Internal hemorrhoids develop when veins in the rectum become swollen or stretched due to increased pressure. Common triggers include chronic constipation, prolonged sitting, pregnancy, and aging. Over time, these veins may prolapse, meaning they extend beyond the anal opening.
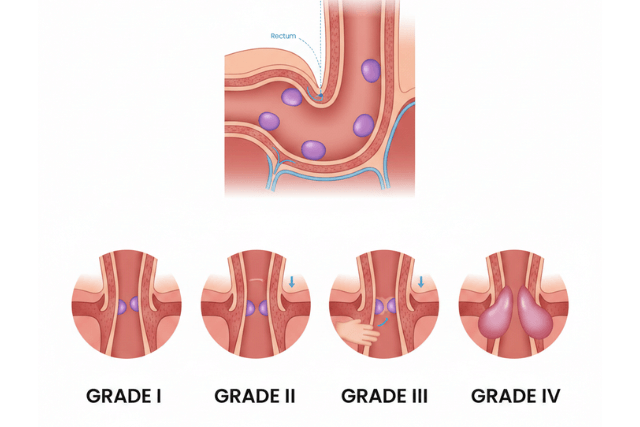
Grades of Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids are classified into four grades based on severity:
- Grade I: Swelling occurs inside the rectum, usually without prolapse.
- Grade II: Hemorrhoids may prolapse during bowel movements but retract on their own.
- Grade III: Hemorrhoids prolapse during bowel movements and require manual retraction.
- Grade IV: Hemorrhoids remain prolapsed and cannot be pushed back inside, often requiring surgical intervention.
Understanding the grade of internal hemorrhoids is crucial for selecting the most effective treatment.
Symptoms of Internal Hemorrhoids
Internal hemorrhoids may not cause immediate pain. However, several symptoms often indicate their presence. In fact, recognizing these signs can prompt timely treatment and help prevent complications.
Common Symptoms
- Rectal bleeding: Bright red blood may appear on toilet paper or in the toilet bowl. Often, this is the first noticeable symptom.
- Prolapse: Tissue can protrude through the anal opening, especially during bowel movements. At times, it may retract on its own.
- Itching or irritation: Mild irritation around the anal area can occur. Additionally, scratching may worsen the discomfort.
- Mucus discharge: A sticky substance may cause further discomfort. Consequently, hygiene becomes important to prevent irritation.
- Sensation of incomplete evacuation: You might feel like the bowel is not fully emptied. Therefore, this can lead to repeated straining during bowel movements.
When these symptoms persist, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. Moreover, early intervention helps prevent progression to severe grades and ensures better management.
Causes of Internal Hemorrhoids
Several factors increase the risk of developing internal hemorrhoids. Understanding these causes can help in prevention and treatment.
Straining During Bowel Movements
One of the most common causes is straining due to constipation. Hard stools increase pressure on the rectal veins, causing them to swell over time.
Chronic Diarrhea
Frequent loose stools also irritate rectal veins, leading to internal hemorrhoid formation.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy increases pressure on pelvic veins, contributing to hemorrhoid development. Hormonal changes further weaken the vein walls.
Aging
As people age, supportive tissues around the rectal veins weaken, making internal hemorrhoids more likely.
Sedentary Lifestyle
Prolonged sitting or lack of regular exercise can increase pressure in the rectal veins, raising the risk of internal hemorrhoids.
Diagnosis of Internal Hemorrhoids
Diagnosing internal hemorrhoids requires a careful medical evaluation. Most patients consult a gastroenterologist or colorectal surgeon to confirm the condition.
Medical History and Physical Exam
The doctor begins by reviewing symptoms, medical history, and risk factors. A digital rectal exam may be performed to assess swelling and prolapse.
Anoscopy
An anoscope is a small, tube-like instrument inserted into the rectum to visualize internal hemorrhoids. This procedure helps determine the grade and severity of the condition.
Additional Tests
In cases of rectal bleeding or unusual symptoms, further testing, such as a colonoscopy, may be recommended to rule out other conditions like colorectal cancer.
Treatments for Internal Hemorrhoids
Treatment options vary depending on the severity of the hemorrhoids. Mild cases often improve with lifestyle adjustments, while severe or persistent cases may require medical or surgical intervention.
Lifestyle Modifications
Lifestyle changes form the foundation of internal hemorrhoid treatment. These include:
- Increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Drinking plenty of water to soften stools
- Avoiding prolonged straining during bowel movements
- Regular physical activity to improve circulation
- Limiting prolonged sitting
Medications
Over-the-counter medications can relieve mild symptoms. These include:
- Topical creams and ointments: Reduce swelling and itching
- Suppositories: Help shrink internal hemorrhoids and ease discomfort
- Pain relievers: Reduce discomfort during flare-ups
Minimally Invasive Procedures
For moderate cases, doctors may recommend office-based procedures:
- Rubber band ligation: A small band is placed around the base of the hemorrhoid to cut off blood flow.
- Sclerotherapy: A chemical solution is injected to shrink the hemorrhoid.
Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP®)
Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP®) is a modern, minimally invasive technique for treating internal hemorrhoids. Using laser energy, LHP® precisely targets hemorrhoidal tissue, reducing swelling and restoring normal vein function. The benefits include:
- Minimal pain compared to traditional surgery
- Faster recovery time
- Reduced risk of complications
- Effective treatment for moderate to severe internal hemorrhoids
Surgical Treatment
For severe internal hemorrhoids, especially grade III or IV, surgical options may be necessary. These include:
- Hemorrhoidectomy: Removal of excess hemorrhoidal tissue
- Stapled hemorrhoidopexy: Repositions the hemorrhoid and reduces blood flow
Surgical interventions are typically performed when other treatments fail or complications arise.
Preventing Internal Hemorrhoids
Preventing internal hemorrhoids primarily focuses on reducing strain on rectal veins and maintaining overall digestive health. Fortunately, adopting simple daily habits can make a significant difference.
Key Prevention Strategies
First, maintain a high-fiber diet, as it softens stools and reduces straining during bowel movements. Additionally, drink plenty of water to stay hydrated and further ease digestion.
Exercise regularly to improve circulation and prevent pressure buildup in the rectal veins. Similarly, avoid prolonged sitting, especially on the toilet, since it increases the risk of formation.
It is also important to respond promptly to bowel urges rather than delaying them. Finally, manage your weight effectively to reduce abdominal pressure and further protect the rectal veins.
By following these strategies consistently, you can significantly reduce the risk of recurrence and, consequently, promote long-term rectal health. Furthermore, combining these measures with regular medical checkups ensures early detection and timely management if hemorrhoids develop.
When to See a Doctor
Timely medical attention is crucial. Seek professional care if you experience:
- Persistent rectal bleeding
- Severe pain or discomfort
- Prolapse that cannot be manually reduced
- Signs of infection, including fever or swelling
- Changes in bowel habits
Early consultation with a gastroenterologist or colorectal surgeon ensures effective treatment and prevents complications.
Living with Internal Hemorrhoids
Many people live comfortably with mild internal hemorrhoids through lifestyle adjustments and proper care. Following medical advice, maintaining a high-fiber diet, and practicing good bathroom habits can manage symptoms effectively.
For patients with moderate to severe cases, procedures like Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP®) provide long-lasting relief with minimal discomfort. With timely treatment and ongoing care, patients can return to daily activities without significant disruption.
Conclusion
Internal Hemorrhoids are a common yet manageable condition. For example, causes range from straining during bowel movements and pregnancy to aging and sedentary lifestyles. In addition, symptoms may include rectal bleeding, prolapse, itching, and discomfort. Therefore, early diagnosis by a qualified doctor is essential for effective management.
Moreover, treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, minimally invasive procedures, and surgical interventions. In particular, Laser Hemorrhoidoplasty (LHP®) offers a modern, minimally invasive solution for moderate to severe cases, providing faster recovery and reduced discomfort.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and seeking appropriate care, patients can manage internal hemorrhoids effectively.